MAAP Framework
Introduction
The MongoDB AI Applications Program (MAAP) framework is a set of libraries that you can use to build your RAG Application using MongoDB and Atlas Vector Search and associated MAAP partners
The repo offers flexibility to its users to set up the RAG application by simply configuring a YAML file(details see below). The repo allows users to choose from various options through the partners' program. The following modules of RAG are made configurable
- Data loaders
- Embedding Models
- Chat LLM Models
- Post query Re-ranker
Reference Architecture Diagram
Below given is the reference architecture of the framework with various components.
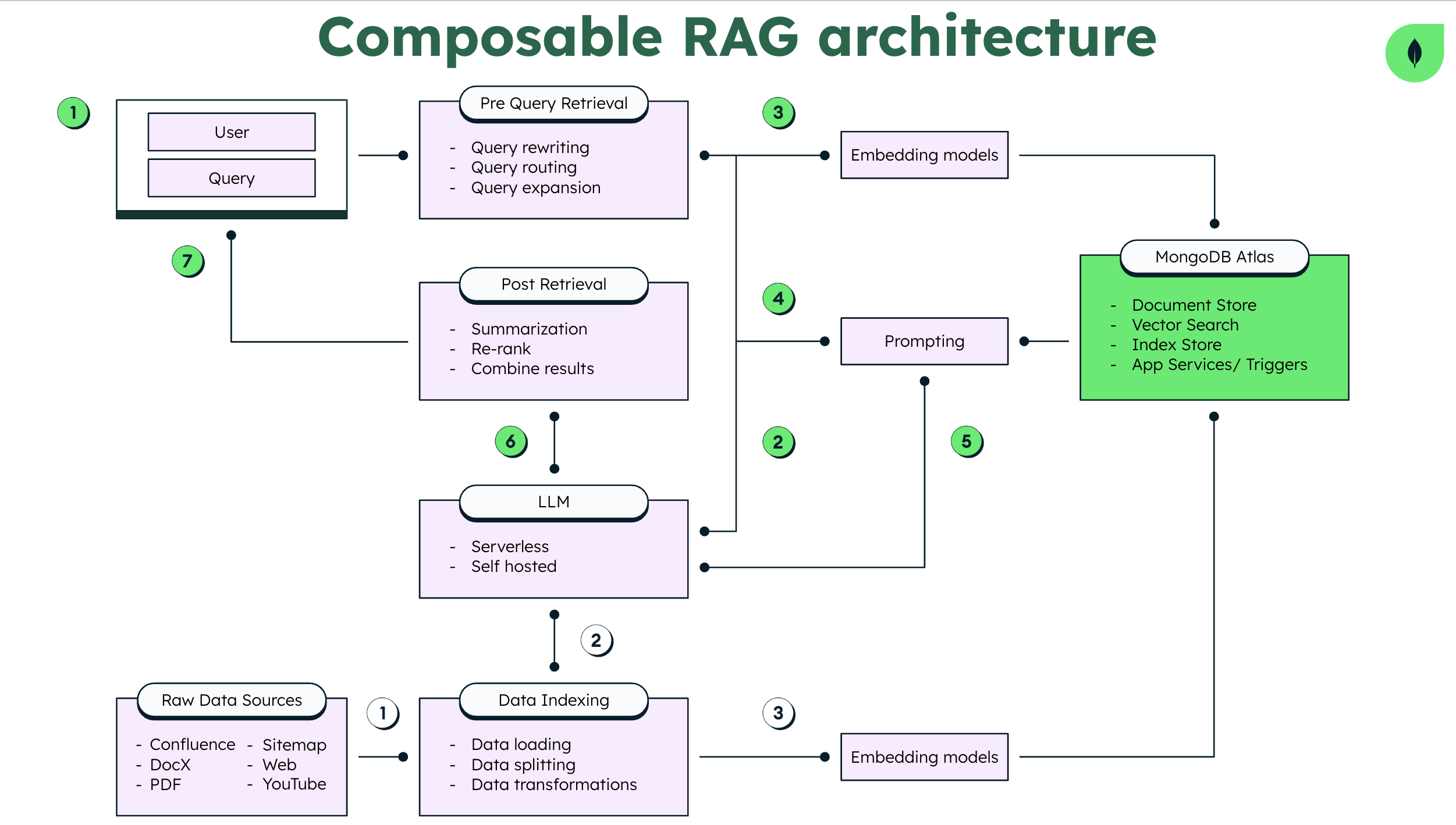
Overview of Advanced RAG Approaches
-
Data Loading
Applications based on Large Language Models (LLMs) often involve extracting data from databases or files, such as PDFs, and converting it into a format usable by LLMs. The pivotal component here is the data source, containing private knowledge or content obtained.
-
Data Indexing and Embedding Models: Chunking & Vectorization
Initially, we construct a vector index to represent the contents of our text documents. This involves breaking down the documents into smaller chunks and converting them into numerical vectors. The vectorized content forms the basis for subsequent retrieval and generation steps.
-
Post Retrieval: Retrieval, Re-ranking & Filtering
After retrieving relevant documents, we refine the context further through re-ranking and filtering:
- Re-ranking: Prioritizing documents based on relevance.
- Filtering: Removing less relevant or noisy documents.
-
Pre Query Retrieval: Query Transformations
Advanced RAG models explore various transformations of user queries to enhance retrieval accuracy. Techniques include query expansion and other modifications.
-
Chat Engine: LLM
The chat engine combines retrieved context with the user’s query to create a prompt for the language model. This prompt guides the language model in generating contextually relevant responses.
-
Chat Engine: RAG Agents
RAG agents manage the entire RAG process, coordinating retrieval, generation, and other components. They ensure seamless interaction between the search index, language model, and other modules.
-
Prompting: Response Synthesizer
The response synthesizer generates the actual answer based on the combined context and user query. Attention and prompt engineering mechanisms may be employed to focus on relevant parts of retrieved documents during generation.
Environment
The application is tested with below configurations.
- Node Version : v20.0+
- MongoDB Version (Atlas) : v7.0 (M10 Cluster Tier)
Document Preface
The MongoDB MAAP Framework documentation provides a comprehensive guide for setting up a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) application using MongoDB and Atlas Vector Search, along with integration options for various MAAP partners. This framework is designed to be highly configurable, allowing users to tailor their applications by simply modifying a YAML configuration file. The framework supports customization in four key areas: data loaders, embedding models, chat LLM (Large Language Models) models, and post-query re-rankers.
The setup process begins with cloning the project and installing dependencies. This involves navigating to the builder/partnerproduct directory, building the project locally, and then installing npm packages in the builder/partner product directory.
Configuration of the RAG application is crucial and involves specifying details for data ingestion, embedding models, vector storage, and LLM models in a YAML file. This includes settings for data source types (e.g., PDF files), paths, chunk sizes, embedding class names, MongoDB connection strings, database and collection names, and specifics about the vector search index and LLM models.
The documentation also highlights the process of instantiating embedding and LLM models based on the configuration. Different classes are instantiated based on the specified class_name in the configuration, catering to various services like VertexAI, Azure-OpenAI, Cohere, and others for embeddings, and a similar approach is taken for LLM models with classes like Fireworks, Anthropic, and Bedrock.
Data loaders play a significant role in how data is ingested into the system. The framework supports multiple types of data loaders (e.g., WebLoader, PdfLoader, SitemapLoader, DocxLoader, ConfluenceLoader), each tailored to handle specific data sources like web pages, PDF files, sitemaps, DOCX documents, and Confluence spaces. These loaders are configured with parameters such as source paths and chunking details, and then added to a data loaders array for processing.
After configuring the application, the user is guided through the process of ingesting data, running the server, and starting the UI client application. The UI client application runs locally, allowing users to interact with the application through a web interface.
This documentation provides a clear and detailed roadmap for developers to set up and customize their RAG applications using the MongoDB MAAP Framework, emphasizing flexibility and ease of use through configuration.
- Setup and Running Demo Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-r824BdVZt0
Steps to run the application
Installation
Clone the project to your machine, and install dependencies.
cd maap-framework
npm install
cd builder/partnerproduct
npm install
Configuration
Edit the config.yaml file to include the necessary details for data ingestion, embedding models, vector storage, and LLM models. The configuration file should include settings for data source types (e.g., PDF files), paths, chunk sizes, embedding class names, MongoDB connection strings, database and collection names, and specifics about the vector search index and LLM models.
For example, the following configuration settings might be included:
ingest:
- source: 'pdf'
source_path: '<file_path>'
chunk_size: 2000
chunk_overlap: 200
embedding:
class_name: Nomic-v1.5
vector_store:
connectionString: '<you_mdb_connection_string>'
dbName: '<db_name>'
collectionName: 'embedded_content'
embeddingKey: 'embedding'
textKey: 'text'
numCandidates: 150
minScore: 0.1
vectorSearchIndexName: 'vector_index'
llms:
class_name: Fireworks
model_name: 'accounts/fireworks/models/mixtral-8x22b-instruct'
temperature: ''
top_p: ''
top_k: ''
systemPromptPath: '<your_system_prompt_file_path>'
aggregate_operators: # This is optional
- connectionString: "<your_mdb_connection_string>"
dbName: '<db_name>'
collectionName: '<collection_name>'
aggregatePipelineName: '<pipeline_name>'
queryFilePath: '<your_mql_query_file_path>'
Also, please make a copy of the builder/partnerproduct/example.env file and rename it as .env. Place this file in the same folder where you are running your application. In the .env file, add the necessary API keys, URLs, connection strings, and any other secrets required for your application.
The following contents are added in the .env (Environment File):
COHERE_API_KEY=
FIREWORKS_API_KEY=
ANYSCALE_API_KEY=esecret_
ANYSCALE_BASE_URL=https://api.endpoints.anyscale.com/v1
BEDROCK_AWS_REGION=us-east-1
BEDROCK_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=
BEDROCK_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=
AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY=
AZURE_OPENAI_API_INSTANCE_NAME=
AZURE_OPENAI_API_EMBEDDINGS_DEPLOYMENT_NAME=
AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION=
AZURE_OPENAI_API_DEPLOYMENT_NAME=
Ensure you source the environment (.env file) by running
. ./.env
After you source the environment, echo any of the environment variables to ensure they are properly sourced. For example run echo $COHERE_API_KEY.
MAAP Partner Integrations
Partner specific information can be found as below; Go to this page for partner specific documentations.
| Sr # | MAAP Partner | Partner Type | Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AWS | Cloud provider | Link |
| 2 | Azure | Cloud provider | Link |
| 3 | GCP | Cloud provider | Link |
| 4 | Anthropic | AI tech | Link |
| 5 | Anyscale | AI tech | Link |
| 6 | Cohere | AI tech | Link |
| 7 | Fireworks.AI | AI tech | Link |
| 8 | Langchain | AI tech | Link |
| 9 | Nomic | AI tech | Link |
Ingest Data
Once configured you can use the yaml file you just created say as in example builder/partnerproduct/src/config.yaml. Run the following from the same terminal as where you sourced .env. Normally this would be under
builder/partnerproduct/src
npm install
npm run ingest <path to your config.yaml>
Go to this page for loader specific documentations.
NOTE: After ingesting your first content, ensure the vector index has been created properly and with the correct vector dimension. You can verify the size of the embedding array on the embedded_content collection, and then set the same size on the numDimensions field of the vector_index.
Run the server
npm run start <full path to your config.yaml>
Start your application UI
You can start your UI client application by running the following command in a separate terminal.
cd builder/partnerproduct/ui
npm install
npm run start
Your application will be running at http://localhost:3000.
Identified Limitations
The following limitations have been recognized within the current framework. These will be addressed in upcoming updates and releases:
- Support for only
.pptxformat inpptdataloader. - Local PDF, PPT, and DOCX files mentioned in the data sources response cannot be opened directly.
collectionName,embeddingKey,textKeyvalues in the.configfile are fixed and cannot be changed.- There might be frequent timeouts in AnyScale LLM.
- Confluence loader fails at authentication.