MongoDB - Confluent Quickstart
Welcome to the MongoDB - Confluent Quickstart for Small Business Loan Agent Chatbot! This repository provides a comprehensive guide to quickly deploy a fully functional chatbot for small business loan assistance. The solution leverages MongoDB, Confluent Cloud, AWS, Anthropic and Flink to deliver a scalable, intelligent, and real-time conversational experience.
This quick start is designed to help businesses streamline their loan application process by providing a chatbot that understands and answers customer queries, retrieves relevant loan documents, and provides actionable insights. The system also includes structured document indexing into MongoDB's vector database, enabling efficient retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to enhance the chatbot's response accuracy.
Key Features
- Real-Time Data Processing: Powered by Confluent Cloud and Flink, ensuring low-latency communication and event-driven architecture.
- Intelligent Conversations: Integrated with Anthropic's AI models for natural and accurate conversational responses.
- Efficient Document Retrieval: Leverages MongoDB Atlas with vector search capabilities for quick and accurate document indexing and retrieval.
- Scalable and Cloud-Native: Built with AWS Lambda for a flexible and serverless REST API.
- Seamless Deployment: Follow step-by-step instructions to deploy the entire solution with minimal effort.
Use Case
This chatbot is tailored for small business loan agents to:
- Provide instant responses to loan-related queries.
- Retrieve structured documents and relevant loan information in real-time.
- Automate repetitive tasks, enabling agents to focus on high-value interactions.
Whether you're exploring new ways to enhance customer engagement or testing generative AI use cases in financial services, this quick start provides the perfect foundation.
👉 Please note that this quick start builds a working AI infrastructure for you, but it's fueled by a small quantity of fake data, so the results won't be at the level that you're accustomed to with AI chatbots like Chat-GPT. Read the Next Steps section at the end of this document to find out how you can tweak the architecture and improve or alter the AI results.
Table of Contents
- GenAI Chatbot Quickstart
Architecture
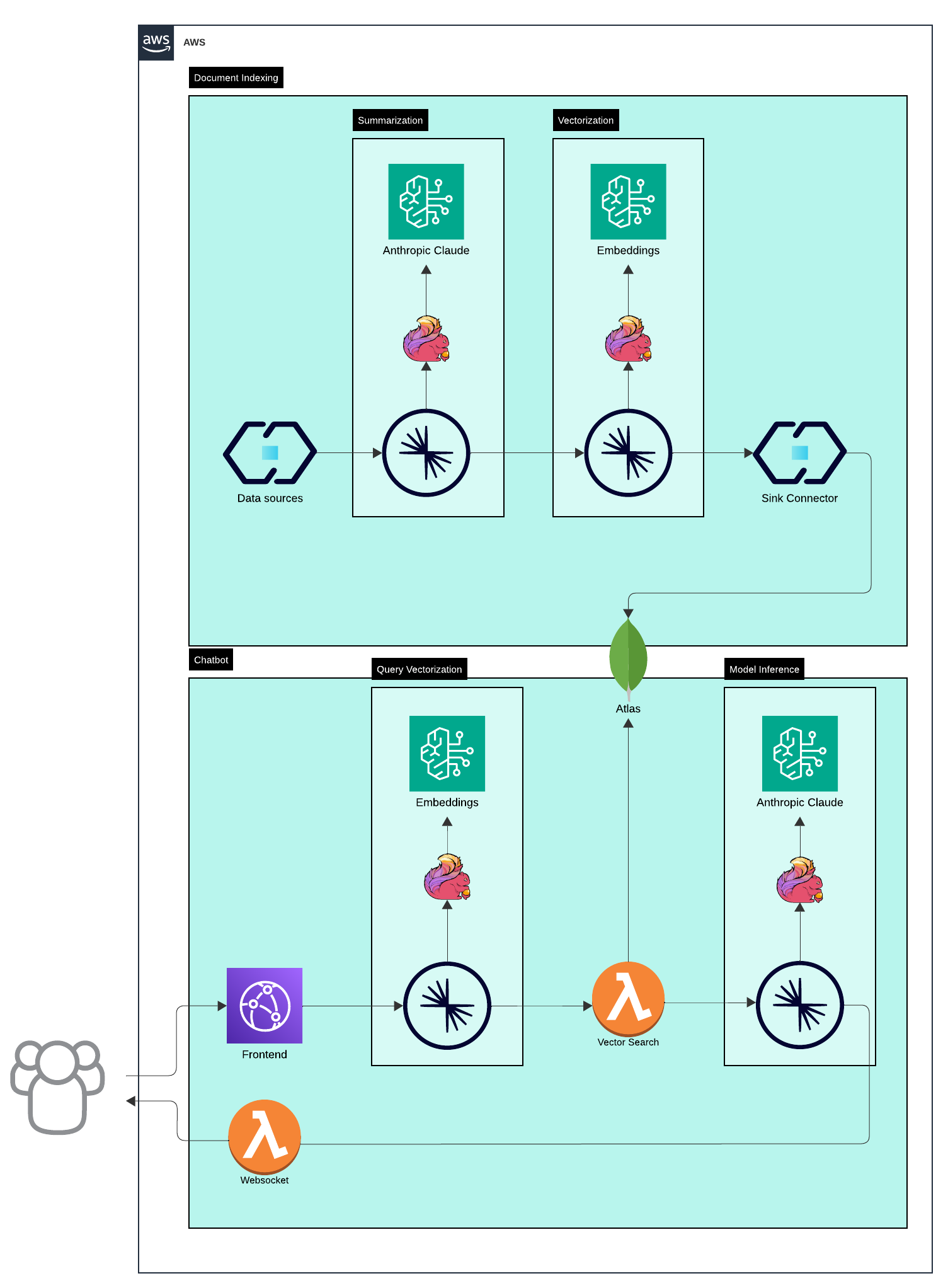
Architecture for handling document indexing and chatbot functionality using a combination of AWS services, Anthropic Claude, MongoDB Atlas and Confluent Cloud. Below is a breakdown of the architecture and its components:
Document Indexing
This section focuses on ingesting and processing data for use in downstream applications like search and chatbots.
- Data Sources: Various data sources feed into the system. These could be structured or unstructured data streams.
- Summarization: Anthropic Claude is used to summarize data to extract meaningful information from documents.
- Vectorization: Embeddings are generated for the input data to convert textual information into high-dimensional numerical vectors.
- Sink Connector: Processed data (both summarized content and embeddings) is output via a sink connector to MongoDB Atlas vector database.
Chatbot
This section demonstrates how the system interacts with user queries in real time.
- Frontend: The frontend handles interactions with users. User inputs are sent to a topic for further processing.
- Websocket: Provides real-time communication between the frontend and backend for immediate responses.
- Query Vectorization: User queries are vectorized using the Embeddings model to transform them into numerical representations. This is done to match queries against stored vectors in the vector search database.
- Vector Search: MongoDB Atlas vector database, retrieves relevant information based on the vectorized query. It searches through embeddings generated during the document indexing phase.
- Model Inference: Anthropic Claude is used for model inference to generate responses.
- Output to User: The system sends the processed results back to the user via the websocket.
Key Concepts
-
Embeddings: These are vector representations of text, allowing the system to handle semantic search.
-
MongoDB Atlas: Enables efficient, scalable, and real-time semantic matching of user queries against high-dimensional embeddings to deliver relevant results in the chatbot and document indexing workflows.
-
Anthropic Claude: Used for both summarization and generating responses in natural language.
Requirements
Docker
The deployscript builds everything for you, the only required software is Docker.
Follow the Get Docker instructions to install it on your computer.
Access Keys to Cloud Services Providers
Once you have docker installed, you just need to get keys to authenticate to the various CSPs.
Confluent Cloud
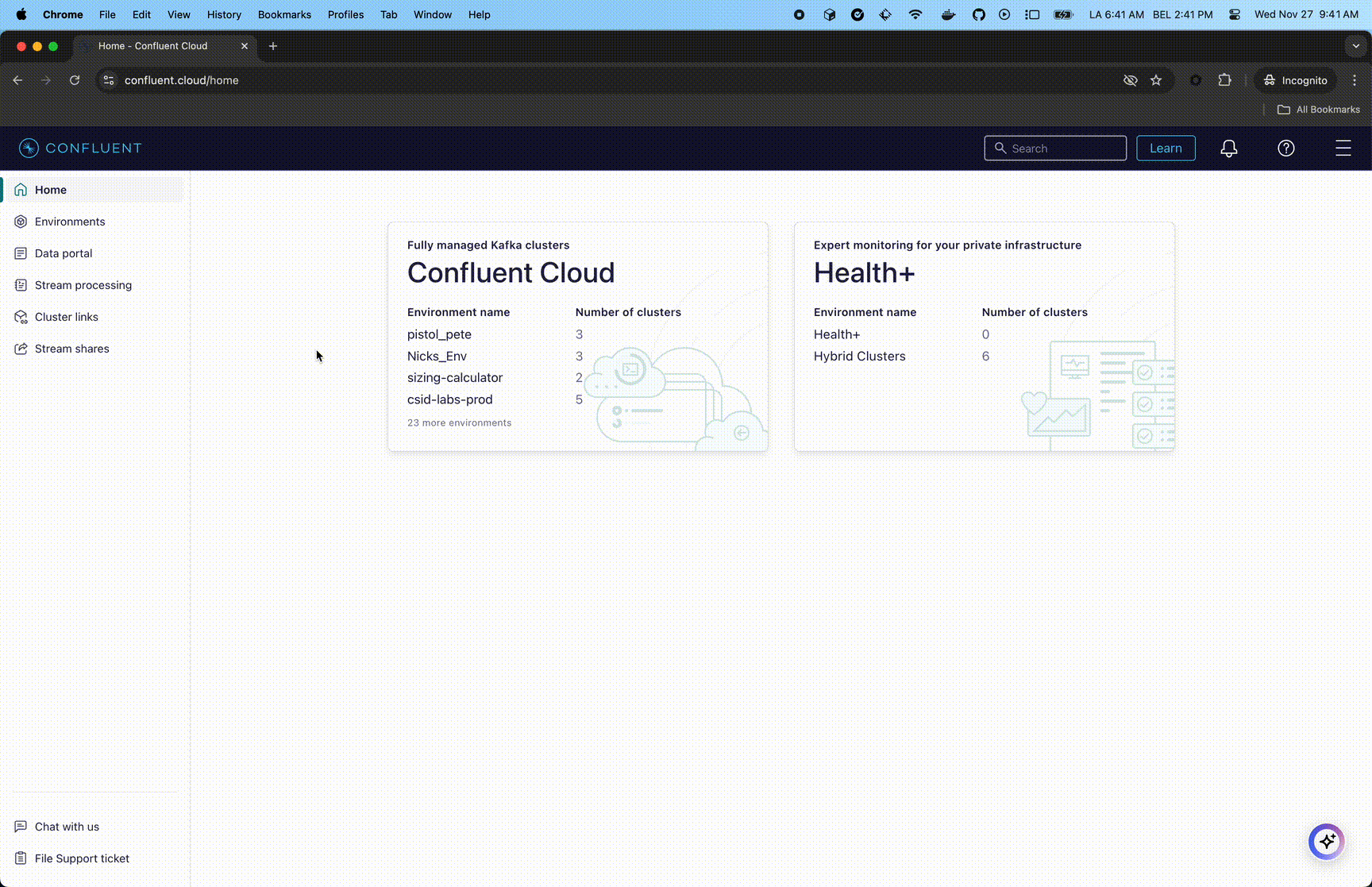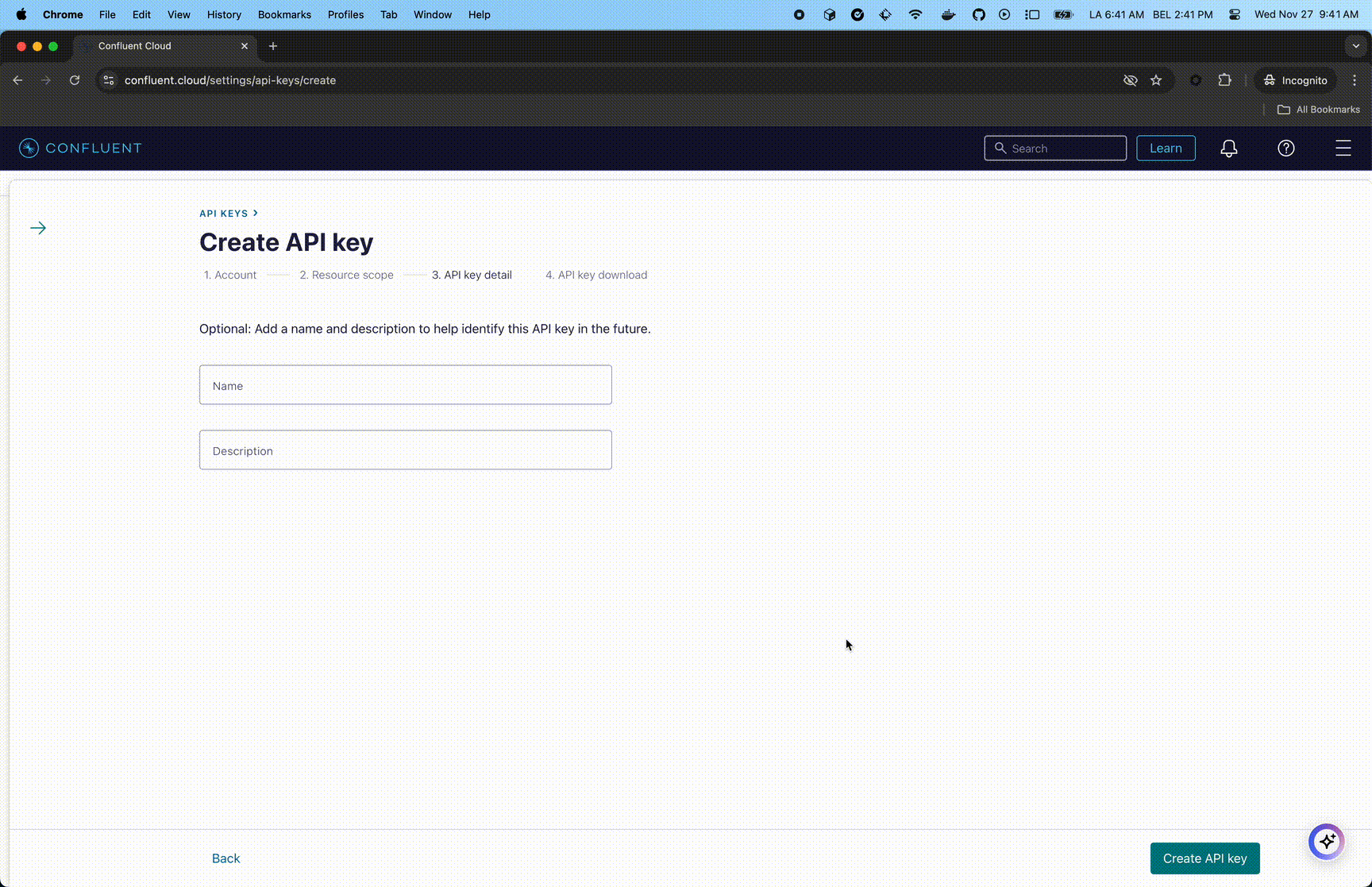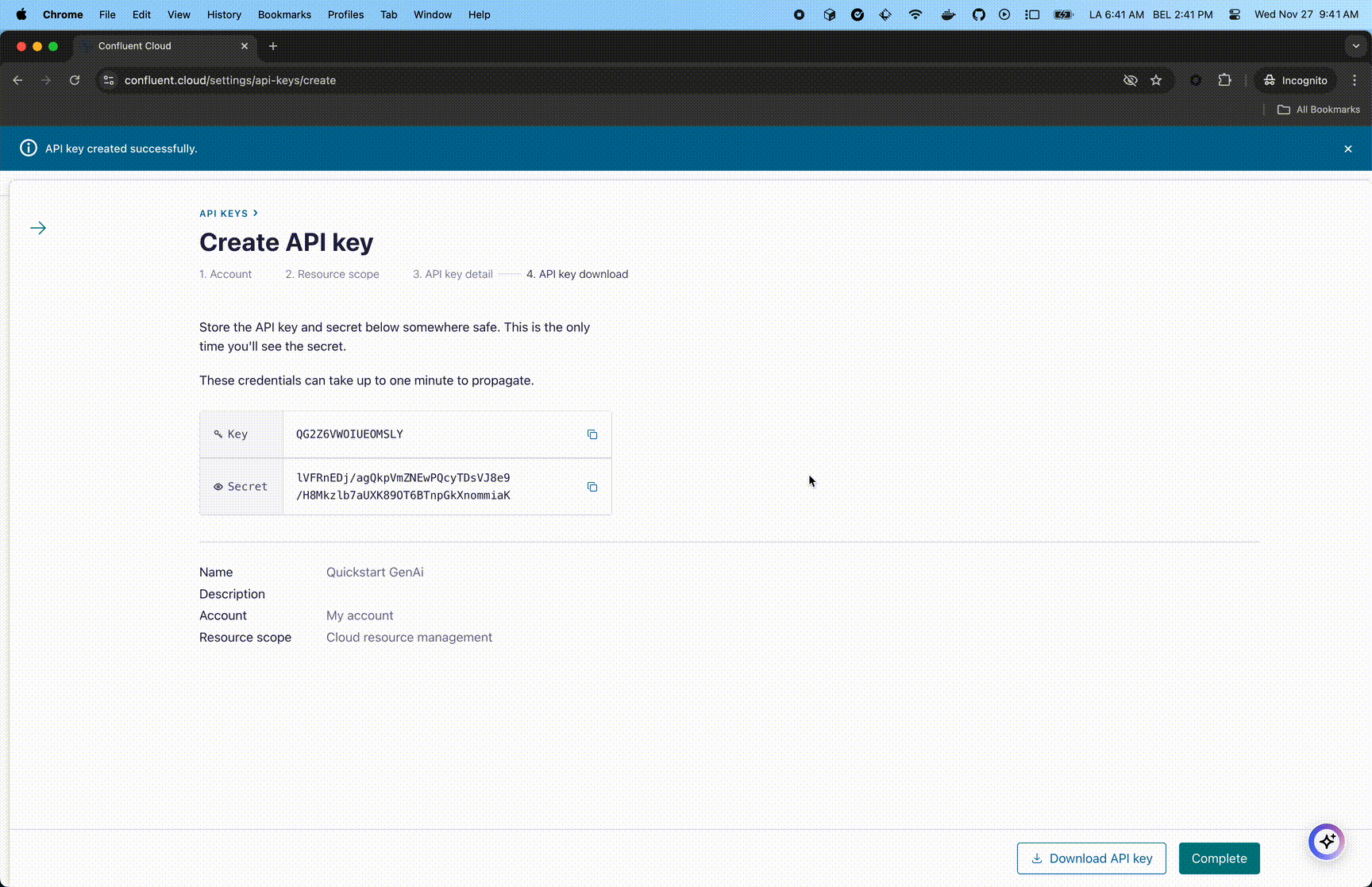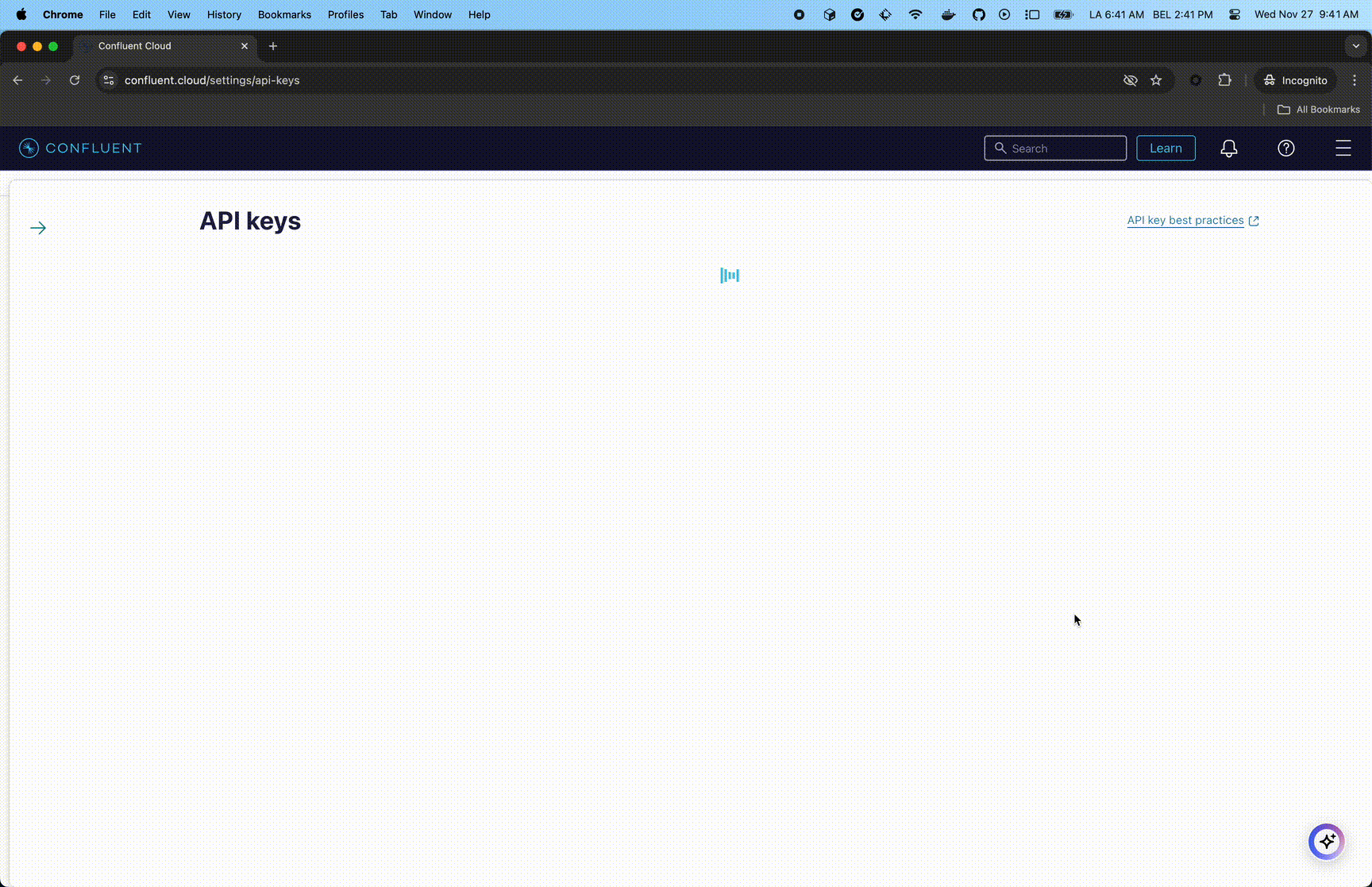
For Confluent Cloud, you need to get a Cloud resource management key.
If you don't already have an account, after signing up, click the top right corner menu (AKA the hamburger menu) and select API keys.
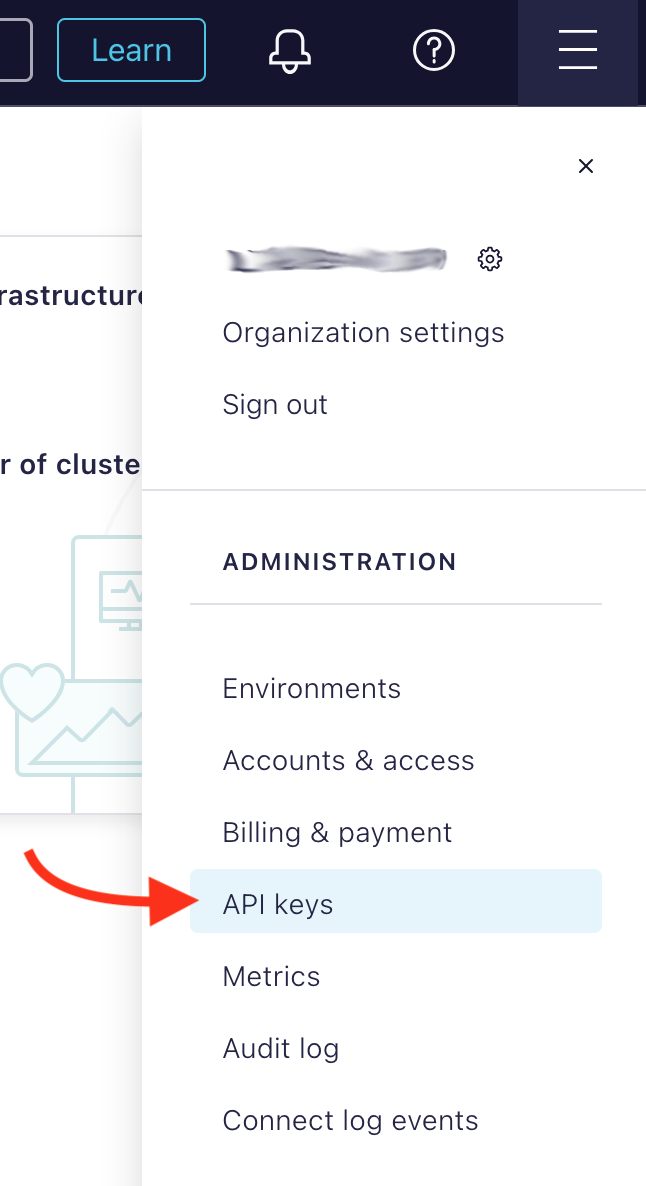 Click the + Add API key button, select My Account and click the Next button (bottom right).
If you feel like it, enter a name and description. Click the Create API Key (bottom right).
Click the + Add API key button, select My Account and click the Next button (bottom right).
If you feel like it, enter a name and description. Click the Create API Key (bottom right).
MongoDB Atlas
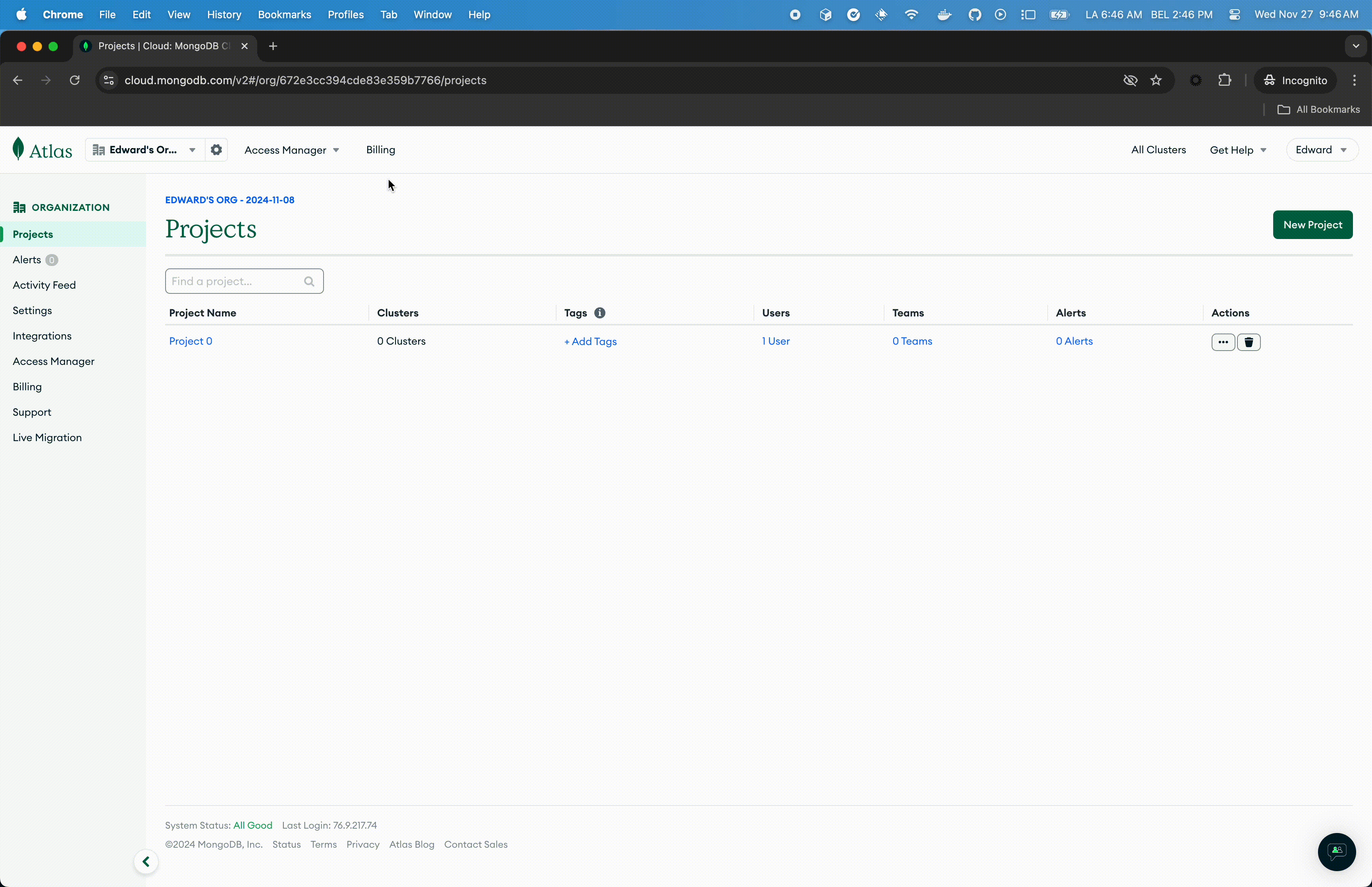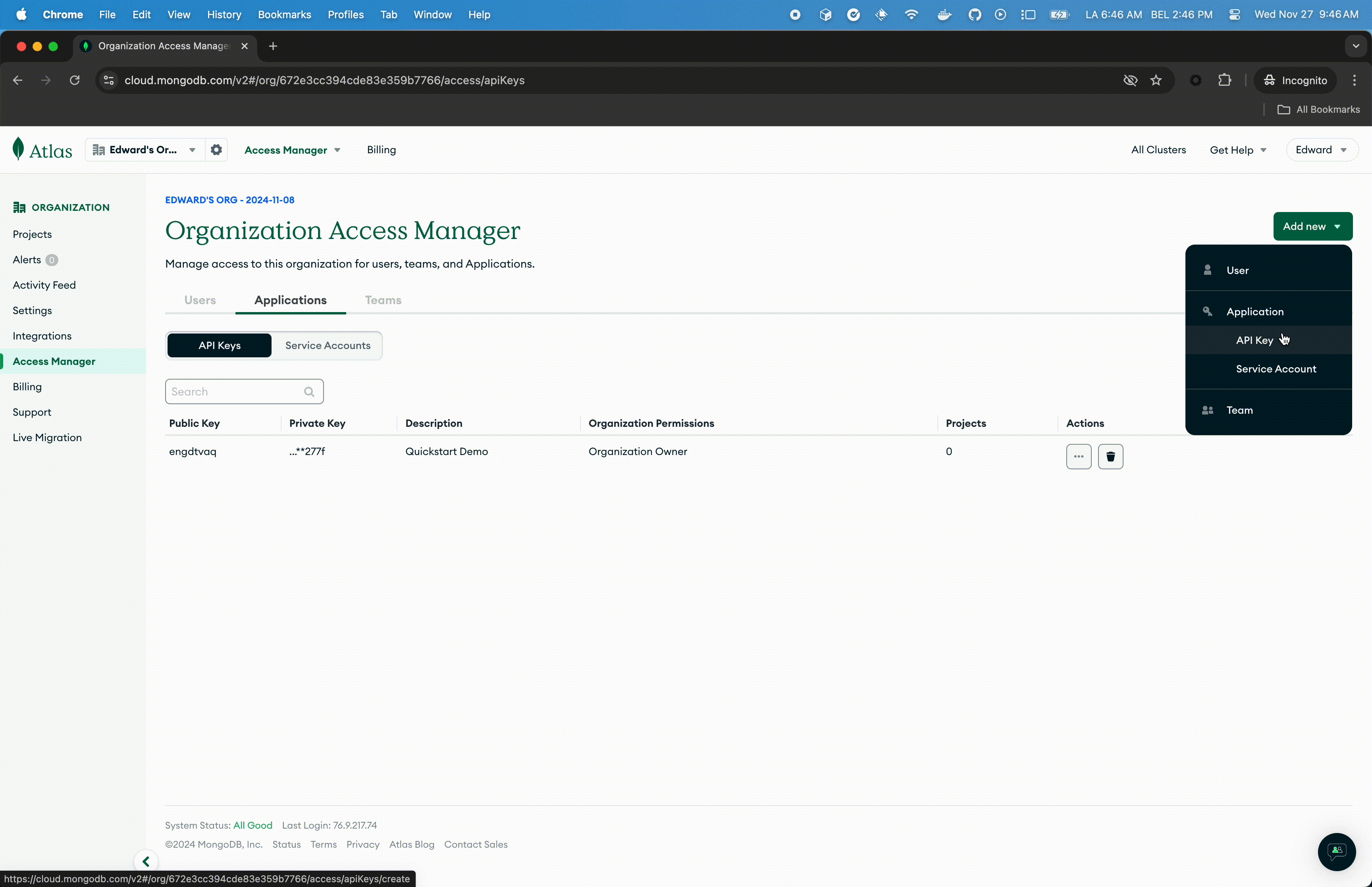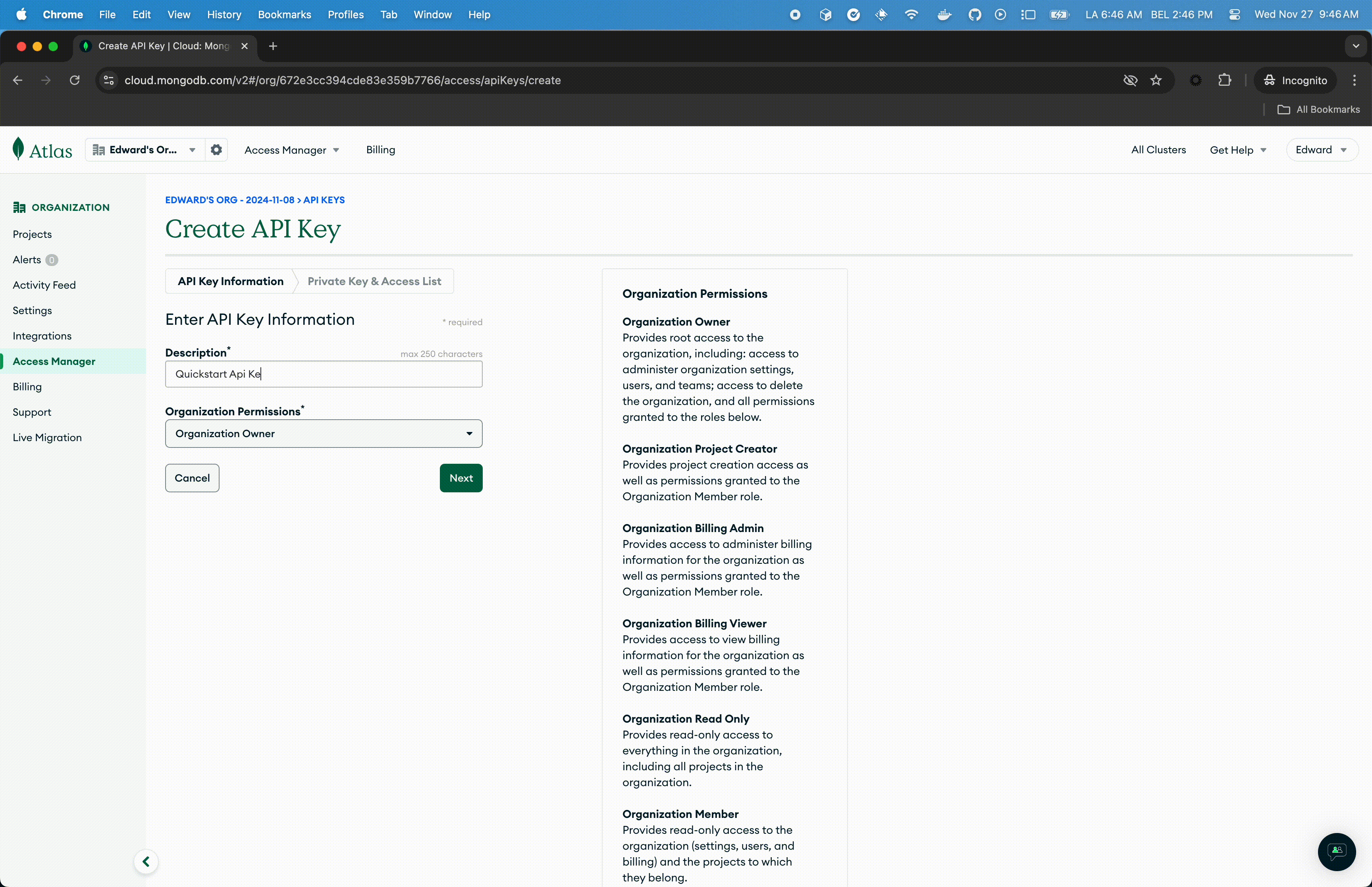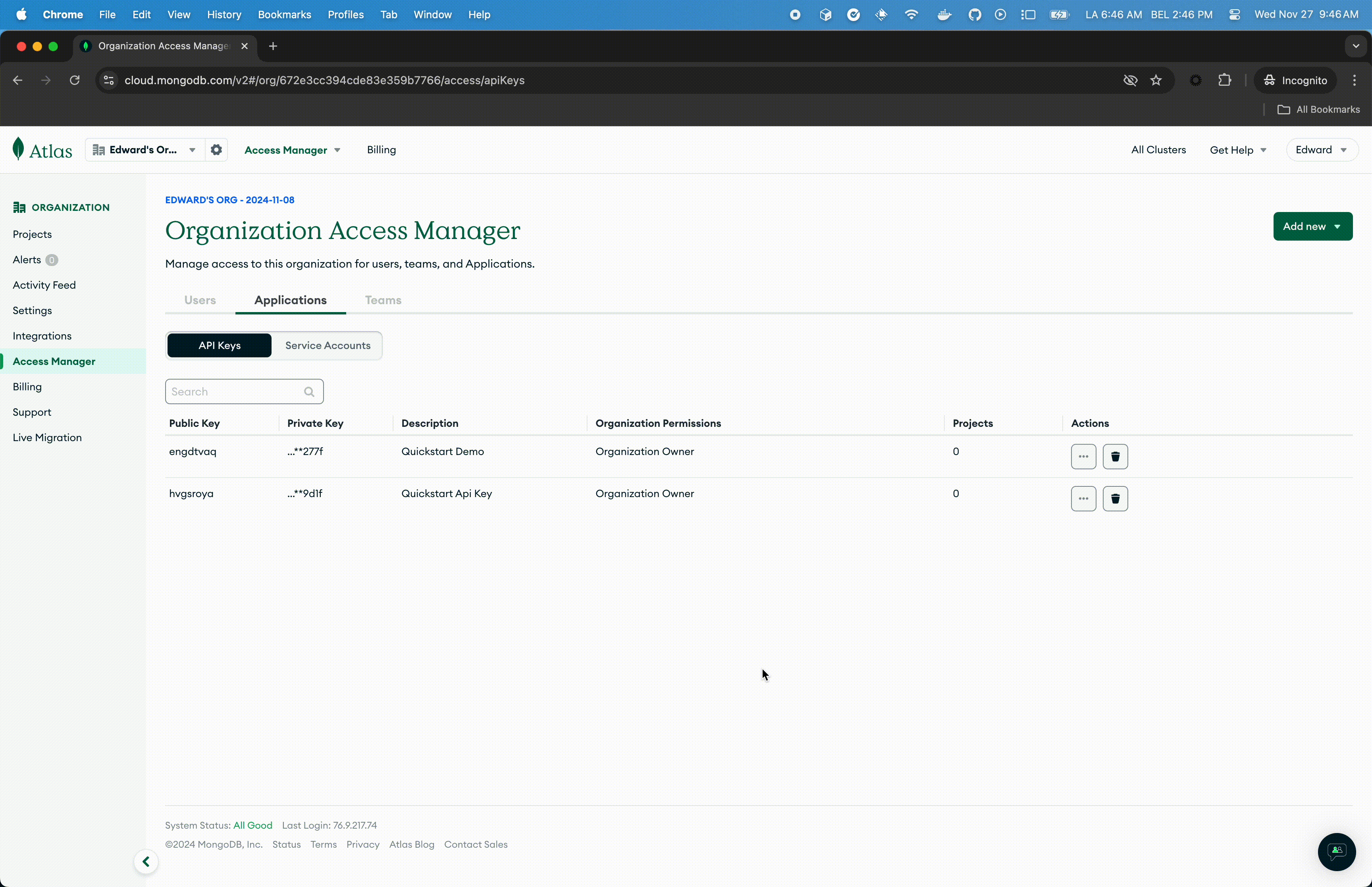
- Connect to the Atlas UI. You must have Organization Owner access to Atlas.
- Select Organization Access from the Access Manager menu in the navigation bar.
- Click Access Manager in the sidebar. (The Organization Access Manager page displays.)
- Click Add new then API Key
- In the API Key Information, enter a description.
- In the Organization Permissions menu, select the Organization Owner role. Important: Make sure that only the Organization Owner role is selected, you may have to click the default Organization Member to un-select it.
- Click Next, copy the public and private key in a safe place and click Done.
Useful links:
- Grant Programmatic Access to an Organization
- MongoDB Atlas API Keys (part of a tutorial on Terraform with Atlas)
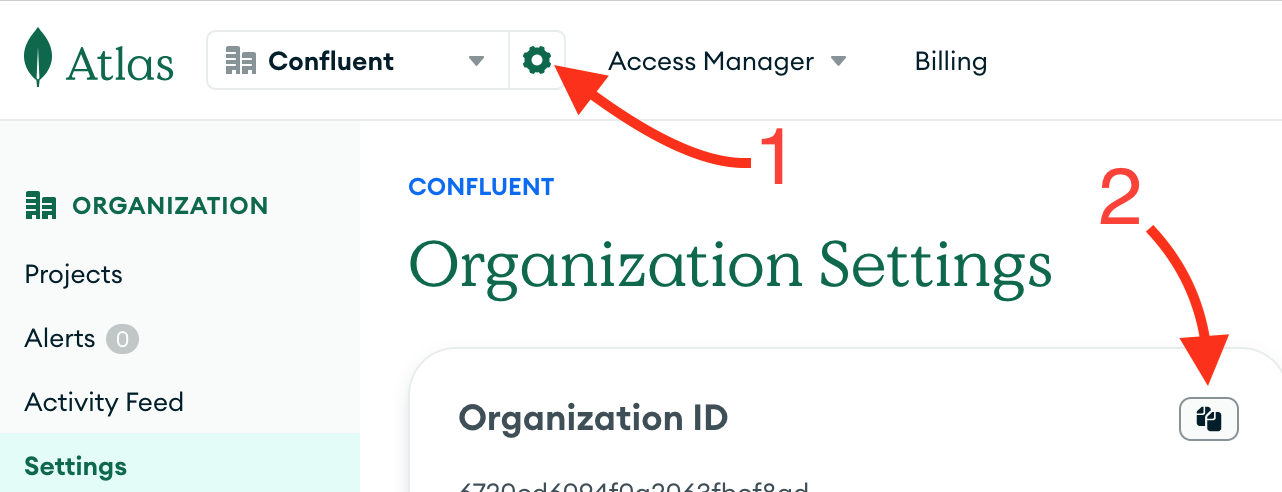
At last, get your Atlas Organization ID from the Atlas UI.
AWS
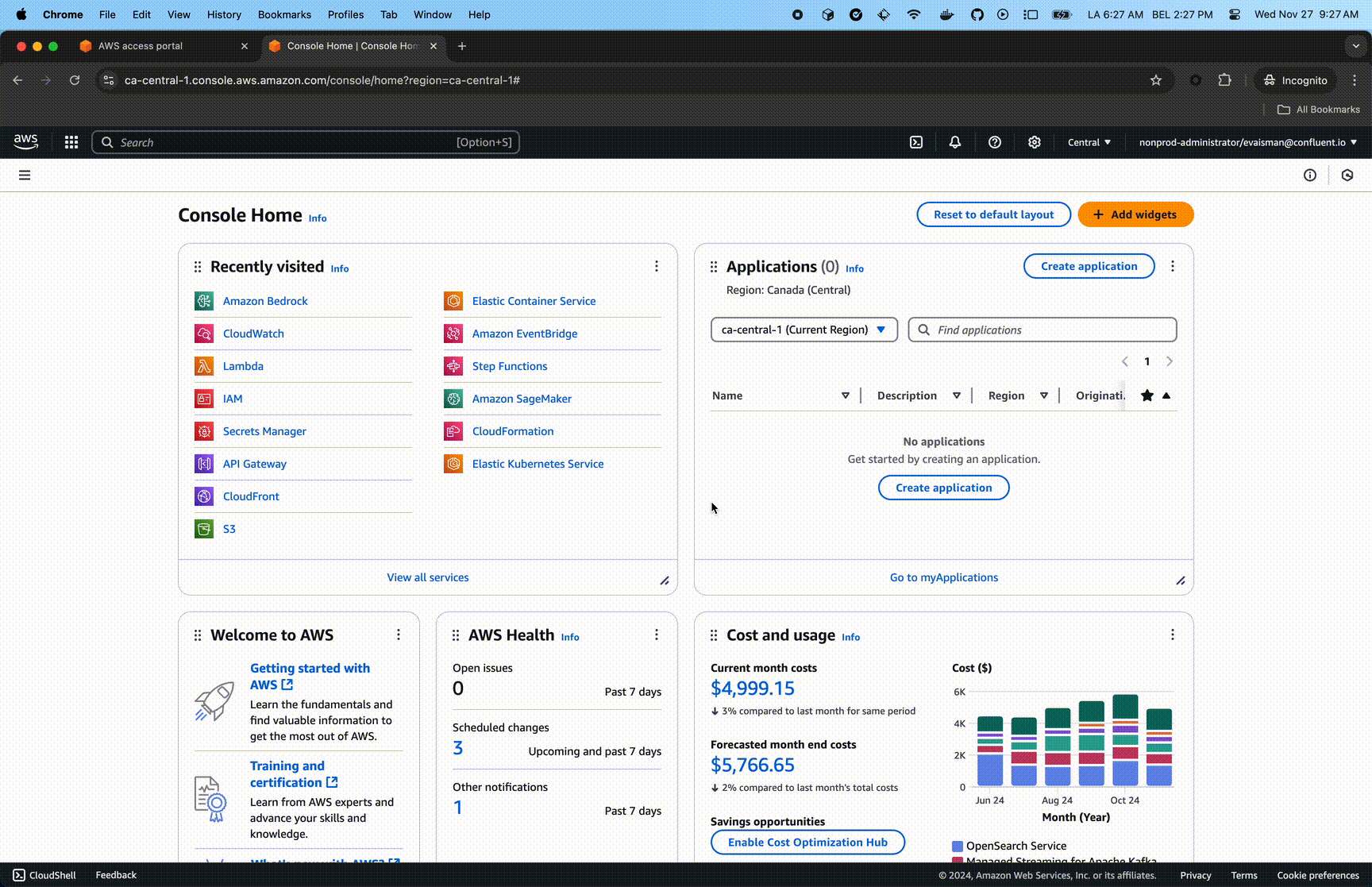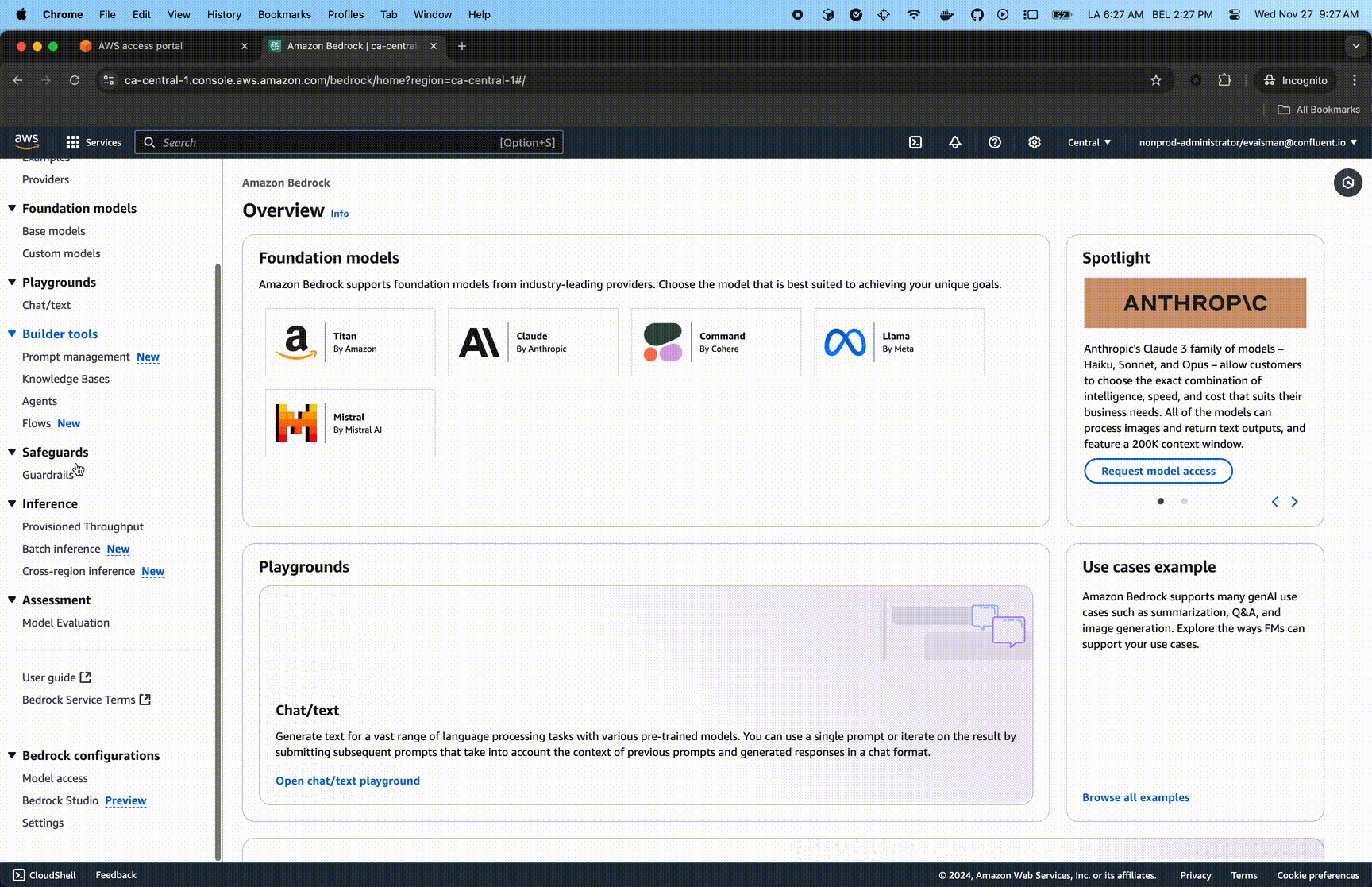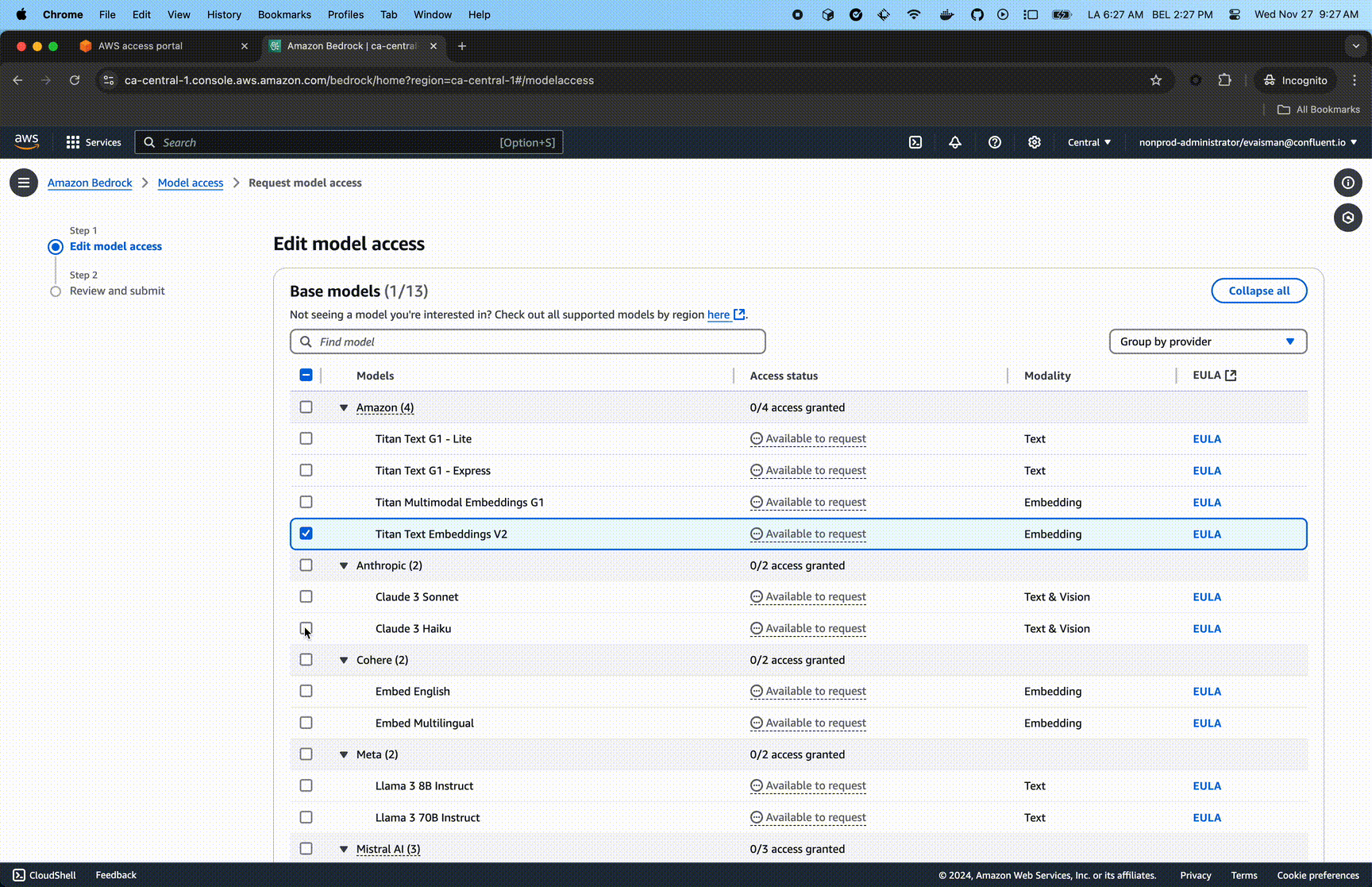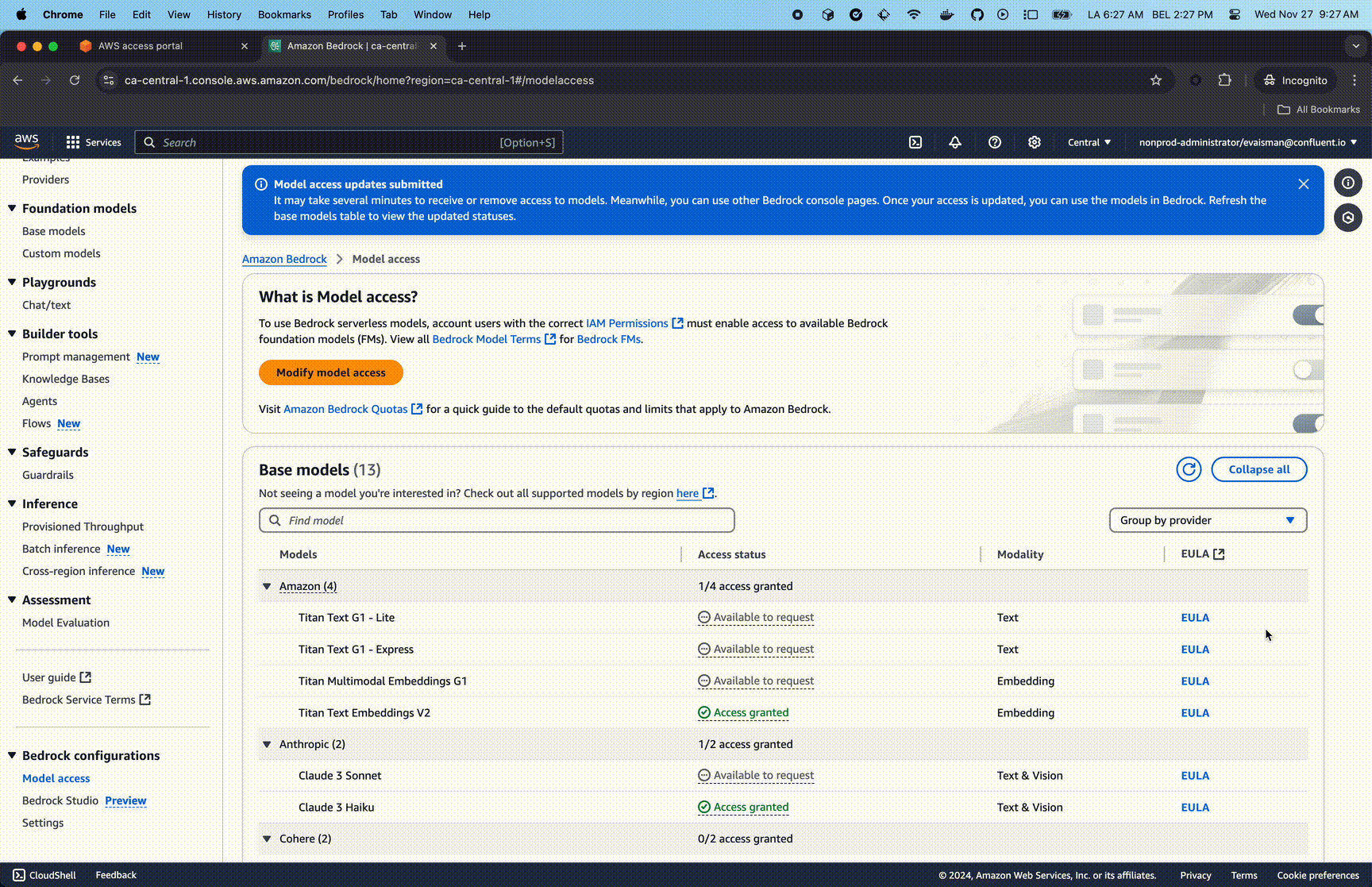
Enable Foundation Model Access
Enable access to amazon.titan-embed-text-v2:0 and anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0 models via the AWS Console.
AWS API Keys
AWS credentials are required for Flink AI to connect to Bedrock, as well as using terraform to deploy resources. You will need a key and secret with appropriate IAM rights.
Managed Policies
If you are using managed policies, Attach the following managed policies to your IAM user or role:
AmazonAPIGatewayAdministrator- Manages and creates the websocket gateway.CloudFrontFullAccess- Exposes the front end via CloudFront.IAMFullAccess- Manages roles and policies for Lambda functions.AWSLambda_FullAccess- Manages Lambda functions.CloudWatchFullAccess- Manages logs and metrics.AmazonS3FullAccess- Manages the S3 bucket for the front end and other Lambda resources.SecretsManagerReadWrite- Manages secrets for Lambda functions.AmazonBedrockStudioPermissionsBoundary- Invokes Bedrock foundational models.
Fine-tuned Policies
For more granular permissions, refer to our cloudtrail events for the exact resources and actions required.
Useful links:
Run the Quickstart
1. Bring up the infrastructure
# Follow the prompts to enter your API keys
./deploy.sh
2. Have a conversation
Once the infrastructure is up and running, you can interact with the chatbot by opening the cloudfront url generated by terraform.
For example, if the terraform output is:
...
frontend_url = "https://d35kqkkhgni7xb.cloudfront.net"
...
You may have the following conversation
For the purposes of this quickstart, any username and password will be accepted, and you'll need to open the chat bubble on the bottom right (after you log in) to have a conversation
2b. Add a new product (Optional)
To showcase our real-time document indexing capabilities, you can add a new document to the system by inserting a new record into the products topic in Confluent Cloud using Flink SQL. This product will then get indexed in MongoDB Atlas and be available for retrieval in the chatbot.
INSERT INTO
`products`
VALUES
(
'00004',
'"small business loan" designed for small business owners to help them with their business expenses. \r\nThe loan amount ranges from $10,000 to $100,000. \r\nThe interest rate is competitive to support small businesses. \r\nRepayment starts immediately after the loan is disbursed. \r\nThe loan term can be up to 5 years. \r\nThe rate table for a "small business loan" is as follows:\r\n\r\n| credit score | rate |\r\n| ------------------- | ---- |\r\n| more than 750 | 4.0 |\r\n| between 500 and 750 | 5.5 |\r\n| between 350 and 500 | 7.0 |\r\n| less than 350 | 9.5 |',
'loan',
'small business loan',
'USD',
'immediate',
'5 years',
'monthly',
'medium',
'active',
'| credit score | rate |\n| ------------------- | ---- |\n| more than 750 | 4.0 |\n| between 500 and 750 | 5.5 |\n| between 350 and 500 | 7.0 |\n| less than 350 | 9.5 |',
'2024-11-01',
'2024-11-01',
'https://www.bigfriendlybank.com/small-business-loan.pdf'
);
3. Bring down the infrastructure
./destroy.sh
Next Steps - Improving the Results
There are numerous actions you can take to influence the responses given by the chatbot:
- Increase the size and the quality of the data set. This demo is built on top of a very small set of insurance products (found in
infrastructure/statements/insert/populate-products.sql), and the description of each product is limited to only a couple of fields. You can also modify the prompt used for summarizing the products ininfrastructure/statements/insert/populate-products-summarized.sql. - Modify the prompts controlling the chat. They are located in:
infrastructure/statements/insert/chat-input-query.sqlandinfrastructure/statements/insert/populate-chat-output.sql - Modify the vectorization and search of the embeddings inside MongoDB Atlas: it's in
infrastructure/main.tf, underresource "mongodbatlas_search_index" "search-vector" {. Check Atlas Vector Search Index Fields and Vector Search Queries for more details. - Modify the parameters of the models, found in
infrastructure/statements/create-models/bedrock-titan-embed.sql. Modifying thetemperatureof the model can yield to more accurate or creative results. Check Anthropic Claude models for more details on the model parameters.
Support and Maintenance
For support:
- Slack @ #ask-maap